

This article is an excerpt from the Shortform book guide to "The Master Guides: Business Innovation" by Shortform. Shortform has the world's best summaries and analyses of books you should be reading.
Like this article? Sign up for a free trial here.
What’s the biggest challenge when coming up with a creative idea for a product? What are the best innovation project management strategies?
Innovation projects present unique challenges when it comes to project management. After all, innovation involves overturning conventions and doing things that have never been done before. To make your product a reality, you must believe that you can successfully manage an innovative project.
Below we’ll discuss how different authors recommend managing innovation projects.
Use a Hypothesis to Manage Innovative Projects
In The Lean Startup, Eric Ries points out that the biggest challenge in project management (especially one that takes the form of a new startup company) is the uncertainty involved in doing something new. His strategy for being successful at innovation project management is basically an adaptation of the scientific method, which he uses to gather data that eliminates uncertainties as efficiently as possible.
First, formulate a hypothesis. What do you believe about your product or your customers that’s vital to your business? Then, build the minimal product necessary to test your hypothesis. Observe the behavior of your prototype or of users who interact with it. Then analyze the data and reflect—how far off was your hypothesis? What do you need to change about your strategy? Should you actually change your entire direction? Based on your conclusions, update your hypothesis or create a new one and repeat the process.
The faster you move through this loop, the faster you’ll learn and the sooner you’ll have enough information to plan and achieve success. (And the less likely the project will be to fail due to financial backers pulling out because they’re not seeing their investment pay off.)
Seven Steps of Innovation Project Management
In 101 Design Methods, Vijay Kumar argues the first step to building a company that can consistently innovate successfully is to believe that it’s possible to plan and manage innovation projects. If you don’t believe that, you’ll probably end up either shying away from innovation projects entirely or letting them run without enough structure to make them successful.
His approach to managing innovation consists of breaking down the innovation process into seven standard tasks that you can plan, schedule, and manage without sacrificing the flexibility that you need on innovation projects:
- Get a clear view of the big picture. Establish the general direction and goals of the project.
- Research your operating environment. Identify your unknowns and plan out how to get the information you need.
- Research your stakeholders. Make sure you understand their motivations and pain points.
- Distill the information you gathered in tasks 2 and 3 into broadly applicable principles that can guide your decision-making.
- Brainstorm ideas that could make up parts of the solution. Relating this to the authors’ 10 types of innovation, each idea would probably be a way to implement one of the 10 types.
- Determine the combination of ideas from task 5 that gives you the best complete solution. This is where you would combine several types of innovation as the authors recommend.
- Create a detailed plan for implementing the final solution, including things like budgets, timelines, and marketing tactics.
While the seven tasks follow a logical progression, understand that sometimes you have to revisit earlier tasks later in the project or cycle through multiple iterations of the whole sequence. As your team completes each task, take stock of the project and decide which task you need to do next. Then plan out how you’ll do the next task (including applicable schedules, budgets, and so forth).
Kumar suggests you keep track of where your project has been and where it’s going using a graphic map that shows the seven tasks and charts your path through them. The map also shows a pair of axes indicating how the focus of the different tasks varies from theoretical to practical and from learning about what already exists to creating new things. Here’s an adaptation of Kumar’s innovation task map, showing a project where you revisited task 2 after first doing task 4, revisited task 6 after first doing task 7, and end up doing two iterations of the full sequence of tasks:
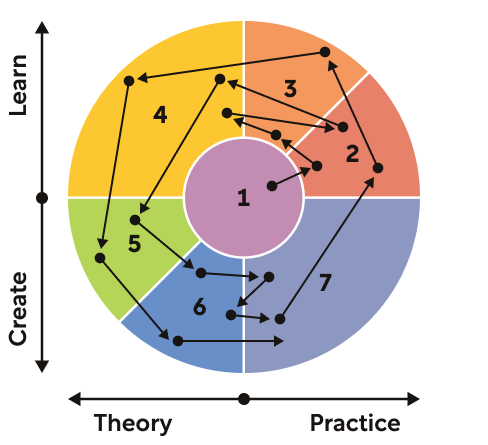
It’s worth noting that while Kumar’s approach to innovation project management is different from Ries’s, the two are not mutually exclusive. On the contrary, Kumar strongly recommends using prototypes for learning and evaluation purposes during tasks 5, 6, and 7.

———End of Preview———
Like what you just read? Read the rest of the world's best book summary and analysis of Shortform's "The Master Guides: Business Innovation" at Shortform.
Here's what you'll find in our full The Master Guides: Business Innovation summary:
- The reason why most innovations never lead to growth or profits
- Key principles for implementing innovative ideas that deliver value
- Advice from seven leading experts on overcoming innovation challenges






